What is a plastic washing line?
.gif) |
A plastic washing line is not a single machine, but a complete set of equipment specially designed for cleaning waste plastics, often referred to as waste plastic washing line equipment. It is like an orderly industrial "assembly line" that cleans and recycles various types of waste plastics through a series of specific processing procedures. These procedures cover multiple links from initial material conveying and crushing, to in-depth cleaning and separation, and finally to dehydration and drying. Each link is completed by corresponding professional equipment, and all equipment work closely and collaboratively, just like a precision-running "industrial orchestra" jointly contributing to the recycling of waste plastics. This integrated system ensures the continuity and reliability of waste plastics from initial processing to final reuse, fully reflecting the efficient collaboration of modern industrial processes. |
What is the use of a plastic washing line?
(I) Resource recycling and reuse
Saving primary resources:
The production of plastics is inseparable from precious primary resources such as oil and natural gas. By recycling and cleaning waste plastics through a plastic washing line, they can be reintroduced into production, which can greatly reduce the exploitation of these primary resources. For example, recycled and cleaned plastics can be used to manufacture new plastic products such as plastic pipes, plastic containers, and plastic furniture. This means that in the production of these new products, there is no need to rely entirely on new raw materials such as oil, thus effectively saving the limited primary resources on the earth.
Reducing production costs:
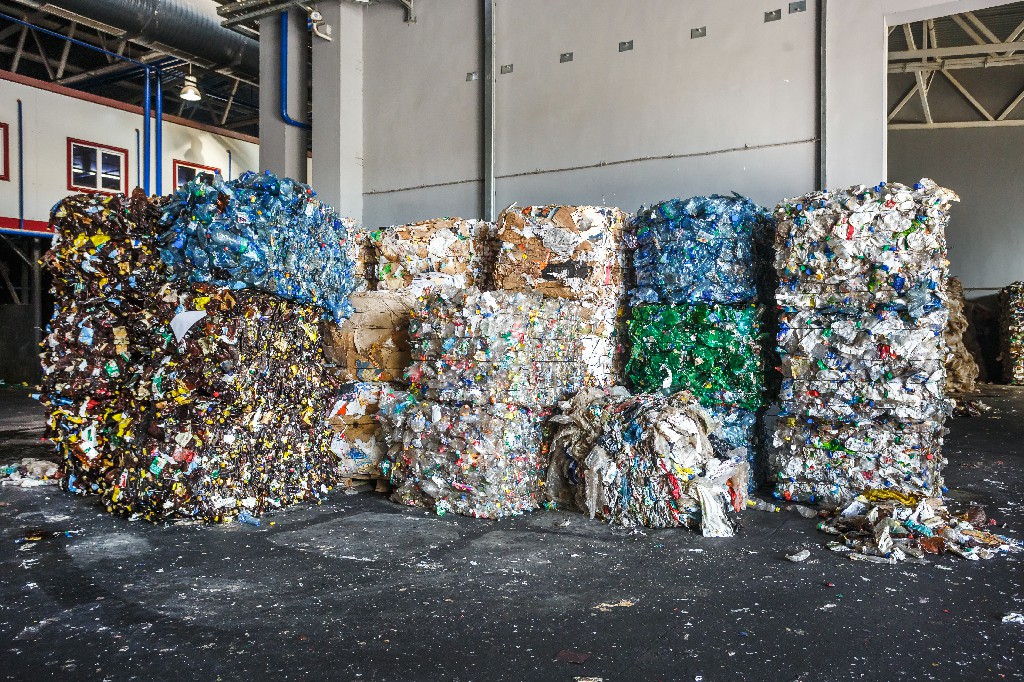 |
For plastic processing enterprises, using waste plastics that have undergone cleaning treatment as raw materials is significantly cheaper than using new plastic raw materials. Because the acquisition cost of waste plastics is relatively low, and after treatment by the washing line, their quality can meet certain production requirements. Enterprises can reduce the procurement cost of raw materials by using recycled plastics on the premise of ensuring product quality, thereby improving economic efficiency. For example, some plastic product factories use recycled and cleaned plastic particles to produce plastic flowerpots, and the cost is 20% - 30% lower than using new plastic particles. |
(II) Environmental protection
Reducing garbage landfilling volume:
If waste plastics are directly landfilled, they are difficult to degrade in the natural environment, which will occupy a large amount of valuable land resources and may pollute soil and groundwater. The application of plastic washing lines enables a large number of waste plastics to be recycled, cleaned and reused, thus greatly reducing the amount of plastic waste that needs to be landfilled. According to statistics, in some regions that actively promote plastic recycling, the annual volume of plastic waste landfilling can be reduced by about 30% - 40% through processing waste plastics with plastic washing lines.
Reducing incineration pollution:
Incineration of plastic waste will produce a large number of harmful gases such as dioxins and furans, which are extremely harmful to the atmospheric environment and human health. Recycling, cleaning and reusing waste plastics through plastic washing lines reduces the need for incineration of plastic waste, thereby reducing air pollution caused by plastic incineration, which is of great significance for improving air quality and protecting the ecological environment.
III. How to use a plastic washing line?
 |
Different types of plastic washing lines have different specific operating procedures, but generally include the following main steps: |
(I) Feeding and pretreatment
Feeding: First, the collected waste plastics need to be transported to the starting end of the plastic washing line through conveying equipment such as a conveyor belt. This process should ensure that the waste plastics can enter the subsequent equipment evenly and stably to avoid blockage or insufficient supply. For example, for a large number of stacked waste plastic films, they need to be manually sorted and placed on the conveyor belt, which is slowly fed into the washing line by the conveyor belt.
 |
Shredding or crushing: Since many waste plastics are large in shape, which is not conducive to subsequent cleaning, they need to be pretreated by a shredder or crusher first. A shredder can tear large pieces of plastic, such as plastic plates and plastic barrels, into smaller pieces or blocks; a crusher can further crush the plastic into smaller particles. For example, putting waste plastic beverage bottles into a crusher, after crushing, the beverage bottles will become plastic fragments of uniform size, which is convenient for subsequent cleaning. |
(II) Cleaning links
 |
Friction cleaning: The crushed plastic fragments enter the friction cleaning machine. Inside the friction cleaning machine, there are high-speed rotating parts. These parts rub against the plastic fragments, and can remove the dirt and impurities attached to the plastic surface through friction. For example, for plastic film fragments stained with soil and oil on the surface, most of the dirt will be stripped off after high-speed friction in the friction cleaning machine. |
 |
Rinsing: After friction cleaning, the plastic fragments then enter the rinsing equipment, usually the rinsing tank. In the rinsing tank, the functions of density separation and cleaning are combined. The floating material (pp/film, woven bag) is driven by the multi-claw rinsing roller to move to the next recovery unit, and the heavy residue impurities in the soft material will be discharged from the bottom sewage outlet. The main impurities of the sediment (pet) are PVC labels and pp/pe bottle cap sealing rings. In the sediment rinsing tank, the pet is driven by the side lifting screw to move to the next recovery unit, and the floating material impurities will be pushed forward by multiple rows of rinsing rollers and have the function of collecting the floating material separately (which can be sold as a by-product) |
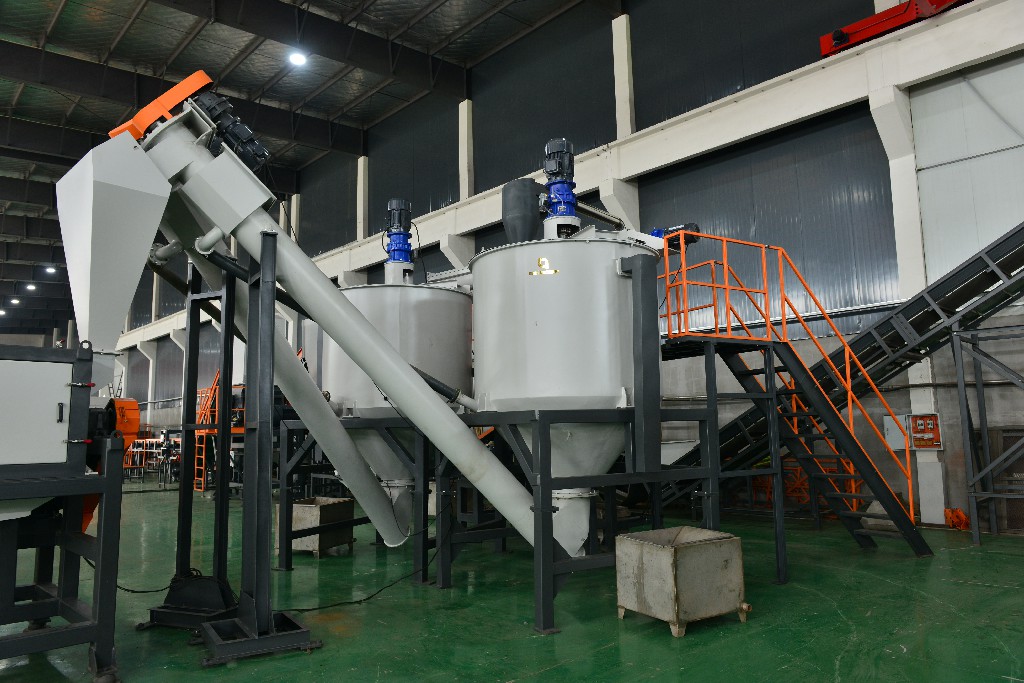 |
Hot washing: For some waste plastics that are seriously polluted and difficult to completely remove stains through conventional washing, a hot washing unit can be added. Add an appropriate amount of detergent (alkali) and hot water to the hot washing tank, soak the plastic fragments in it, and use friction and chemicals to separate stubborn pollutants such as oil and glue. However, hot washing requires strict control of the concentration of the detergent and the washing time to ensure the cleaning effect and avoid damage to the plastic itself. |
(III) Dehydration and drying
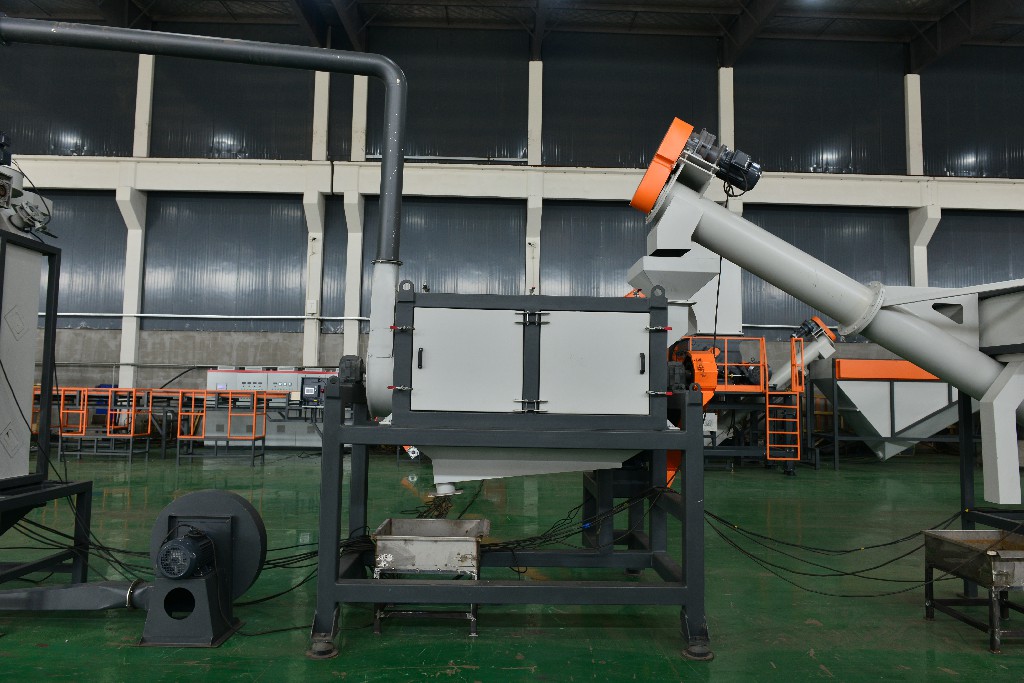 |
Centrifugal dehydration: The cleaned plastic fragments contain a lot of water and need to be dehydrated first. The centrifugal dehydrator uses the centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation to throw out most of the water in the plastic fragments. For example, putting the cleaned plastic film fragments into a centrifugal dehydrator, after several minutes of high-speed rotation, the water content of the plastic film fragments can be reduced to a certain extent, which is convenient for subsequent drying. |
 |
Hot air drying: The plastic fragments after centrifugal dehydration still contain a small amount of water and need to be further dried by hot air drying equipment. In the hot air dryer, hot air continuously blows the plastic fragments to make the water evaporate quickly. After hot air drying, the water content of the plastic fragments can be reduced to meet the standards required for subsequent processing, generally to about 1% - 5%. In this way, the dried plastic fragments can be stored as clean recycled plastic raw materials or further processed. |
(IV) Discharging and subsequent treatment
The clean plastic fragments after drying are transported to the designated container or storage area through the discharging device. These recycled plastic raw materials can be directly sold to plastic processing enterprises for manufacturing various plastic products; they can also be processed into plastic particles through equipment such as granulators according to needs, so as to facilitate storage and transportation and provide high-quality raw materials for subsequent plastic production.
What are the characteristics of a plastic washing line?
(I) Efficiency
Fast processing speed: Modern plastic washing lines usually have high production efficiency and can process a large amount of waste plastics per hour. For example, some large-scale plastic washing lines can process 1 - 5 tons of waste plastics per hour, which can meet the needs of large-scale recycling enterprises. This is due to its advanced equipment design and reasonable process flow, with all links closely connected, which greatly shortens the residence time of waste plastics in the washing line and improves the overall processing speed.
Good cleaning effect: Through the combination of various cleaning methods such as friction cleaning, rinsing and chemical cleaning, the plastic washing line can effectively remove various dirt, impurities and labels on the surface of waste plastics, so that the cleaned plastics can reach a high degree of cleanliness. Taking the cleaning of waste plastic beverage bottles as an example, after treatment by the washing line, the dirt, glue and label residues on the surface of the bottle flakes can be basically completely removed, reaching the standard that can be directly used for reproduction.
(II) Strong adaptability
Able to handle multiple plastic materials: The plastic washing line can adapt to different types of plastic materials, whether it is common polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or some engineering plastics such as polycarbonate (PC), etc., can be effectively cleaned. This makes it have strong versatility in the face of the complex and diverse waste plastic recycling market, and can meet the needs of different customers for cleaning plastics of different materials.
Adapting to different pollution degrees: Whether it is lightly polluted waste plastics or plastics that have been exposed to harsh environments for a long time and are seriously polluted, the plastic washing line can achieve good cleaning effect through corresponding process adjustments and equipment combinations. For lightly polluted plastics, simple physical cleaning may be sufficient; for seriously polluted plastics, links such as chemical cleaning can be added to ensure that the cleaned plastics meet the reuse standards.
(III) Energy conservation and environmental protection
Recycling of water resources: Many plastic washing lines are equipped with a complete sewage recycling system. The sewage generated during the cleaning process can be reused in the cleaning link after a series of treatments such as precipitation, filtration and purification, which greatly reduces the consumption of fresh water resources. For example, some advanced plastic washing lines can achieve a water recycling rate of more than 80% - 90%, which not only saves water resources, but also reduces production costs and environmental pollution.
Low energy consumption: With the continuous progress of technology, plastic washing lines pay more and more attention to energy conservation in design. The use of high-efficiency motors, optimized equipment structure and reasonable process flow significantly reduces the energy consumption of the equipment during operation. Compared with early cleaning equipment, modern plastic washing lines can reduce energy consumption by 30% - 50% when processing the same amount of waste plastics, which is more in line with the requirements of sustainable development.
(IV) High degree of automation
Reducing manual intervention: At present, most plastic washing lines have achieved a high degree of automatic control. From material conveying, equipment start-up and shutdown, to parameter adjustment and fault alarm in the cleaning process, they can be accurately handled by the automatic system. This not only significantly reduces the workload and labor intensity of manual operation, but also greatly improves the stability and accuracy of the production process. For example, operators only need to preset parameters on the console, and the equipment can automatically operate according to program instructions to efficiently complete the cleaning of waste plastics.
Improving production stability:The automated control system has real-time and accurate monitoring capabilities, and can track and detect the operating status of the equipment in all directions. Once the equipment fails, the material is blocked, or any other abnormal conditions occur, the system will respond immediately, quickly trigger the alarm mechanism, and simultaneously start the preset emergency disposal process, effectively cutting off the risk chain that may cause production interruptions and ensuring the continuous and stable operation of the production line. In addition, automated control technology plays a vital role in the cleaning process. It can ensure that the key parameters in the cleaning process, such as temperature, pressure, flow, etc., continue to remain within the pre-set optimal range with extremely high accuracy and strong stability. This precise control not only significantly improves the high consistency of the cleaning effect, so that each cleaning can meet the expected standards, but also greatly guarantees the stability and reliability of product quality, laying a solid foundation for the company's efficient production and high-quality product output.
What are the categories of plastic washing lines?
|
Classification basis |
Category name |
Applicable plastic type |
Main equipment and process characteristics |
Typical application scenarios |
|
Classification by processed plastic material |
Soft plastic washing line |
Agricultural films, plastic packaging films, sunshade nets, fishing nets, PP woven bags, plastic bags, cement bags and other soft plastics |
Equipped with a special shredder to shred soft plastics; multiple friction cleaning and rinsing to ensure dirt removal. The equipment includes spiral cleaning machine, friction cleaning machine, centrifugal dehydrator, hot air dryer, etc. |
Waste agricultural film is cleaned and recycled, and converted into raw materials that can be used to produce new plastic film or other plastic products |
|
Classification by processed plastic material |
Hard plastic washing line |
Plastic housings of household appliances, plastic bottles, plastic barrels, plastic helmets, computer housings, TV housings, plastic tables and chairs, plastic pipes and other hard plastics |
If there are few metal impurities, a heavy crusher can be used directly. The process includes unpacking, shredding, crushing, pre-washing, rinsing, friction washing, centrifugal dehydration, magnetic roller (metal remover), etc. |
Plastic turnover baskets, blue barrels, etc. remove conventional impurities to obtain clean crushed materials for re-production |
|
Classification by cleaning process |
Physical cleaning line |
Waste plastics with less surface contamination, such as plastic films with only a small amount of dirt and dust |
Rely on physical processes such as shredding, crushing, friction, rinsing, centrifugal dehydration, hot air drying, etc. to clean. The process is simple, environmentally friendly, and the equipment cost is low. |
Cleaning of slightly contaminated waste plastic films, plastic packaging bags, etc. |
|
Classification by cleaning process |
Chemical cleaning line |
Waste plastics with severe pollution and stubborn stains, such as plastic labels with a lot of glue on the surface |
Chemical cleaning agents are used to dissolve stubborn pollutants such as oil, glue, and ink. The concentration of cleaning agents must be strictly controlled, and wastewater must be properly handled. The equipment and operating costs are high. |
Cleaning of waste plastic label paper to remove stubborn stains such as glue on the surface |
|
Classification by cleaning process |
Physical and chemical combined cleaning line |
Waste plastics of various contamination levels and materials |
Combining the advantages of physical and chemical cleaning, first use physical means to remove most of the dirt, and then use chemical cleaning agents to deal with stubborn stains. Good cleaning effect and wide application |
Waste plastic beverage bottle cleaning, comprehensive physical crushing, rinsing and chemical cleaning to remove dirt, labels and glue |
Plastic washing lines can be classified in many ways according to different standards. The following table presents the details of different categories and their characteristics:
What are the advantages of plastic washing lines compared with similar equipment?
To clearly show the advantages of plastic washing lines, the following table compares them with simple manual cleaning and traditional simple cleaning equipment:
|
Compare Projects |
Plastic washing line |
Simple manual cleaning |
Traditional simple cleaning equipment |
|
Cleaning efficiency |
Processing hundreds of kilograms or even tons of waste plastics per hour, large washing lines can process 1-5 tons per hour |
A skilled worker can only clean a few dozen kilograms a day. |
The processing capacity is limited, far lower than that of plastic washing lines |
|
Cleaning effect |
Through a variety of professional equipment and scientific processes, it can be fully and deeply cleaned with high cleanliness to meet high standards of reuse needs |
Due to the limitation of manpower and tools, it is difficult to clean thoroughly, and stubborn stains and hidden impurities are not easy to remove |
The cleaning effect is average, and may only remove some surface dirt, but cannot handle stubborn stains |
|
cost |
The initial equipment investment is high, but the unit cost is low in long-term large-scale production, which can reduce labor and time costs |
No equipment investment in the early stage, but high labor costs, low efficiency, and high unit cleaning costs |
The equipment cost is relatively low, but the function is single and may require additional processing steps, so the overall cost is high. |
|
Functional diversity |
Complete equipment system, covering multiple functional modules such as feeding, crushing, cleaning, dehydration, drying, etc. |
Only rely on manual operation, single function |
Single function, may only have simple cleaning or crushing function |
|
Degree of automation |
High degree of automation, which can realize automatic material transportation, automatic equipment operation and automatic parameter control |
Completely dependent on manual operation |
Most of them require frequent manual operations, and the production stability is poor |
|
Environmental performance |
Equipped with a complete sewage treatment system and energy-saving devices, the water resource recycling rate can reach more than 80%, and the energy consumption is low |
There are no environmental protection measures, and the waste generated is directly discharged |
Lack of environmental protection design, direct discharge of sewage, serious waste of water resources, high energy consumption |
How to maintain and maintain the plastic washing line?
(I) What should be done for daily maintenance?
Equipment cleaning: After daily production, clean the exterior of each equipment of the plastic washing line to remove dust, plastic debris and other debris on the surface, so as to prevent these debris from entering the equipment and affecting normal operation. For parts that are easy to scale, such as the rinsing tank and the inside of the friction cleaning machine, they should be thoroughly cleaned regularly to avoid dirt accumulation affecting the cleaning effect.
Component inspection: Check whether the conveyor belt is worn or cracked, and replace it in time if it is damaged; check whether the transmission parts of the equipment such as chains and gears are loose or worn, and fasten and lubricate them in time. Check whether the electrical lines are damaged or aging to ensure the electrical safety of the equipment.
Lubrication maintenance: According to the requirements of the equipment operation manual, regularly lubricate each lubrication point such as bearings and guide rails, use appropriate lubricating oil or grease, and control the amount of lubricant to avoid affecting the normal operation of the equipment due to too much or too little.
(II) What are the contents of regular maintenance?
Equipment debugging: Every once in a while (such as every quarter), debug and calibrate the various operating parameters of the plastic washing line to ensure that the equipment operates in the best state. For example, adjust parameters such as the crushing force of the crusher, the rotating speed of the friction cleaning machine, and the temperature of the hot air dryer to ensure the cleaning effect and production efficiency.
Replacement of vulnerable parts: According to the frequency of equipment use and the service life of vulnerable parts, regularly inspect and replace worn parts such as screens, blades and sealing rings to prevent equipment failures, reduce downtime and maintain the stable operation of the washing line.
Why is it necessary to use a hot wash unit to remove oil stains?
The viscosity of oil, lubricating oil and other oils on the plastic surface decreases significantly as the temperature rises. Experimental data show that when the water temperature rises from 20°C to 85°C, the solubility of oil on the surface of PE film increases by more than 3 times. This is because the intermolecular forces of oily pollutants weaken at high temperatures, making it easier to peel off from the plastic surface.
A recycling plant once tried to clean PP woven bags contaminated with mechanical oil stains with room-temperature water. As a result, 40% of the oil stains remained after 30 minutes of friction cleaning; when using 90°C hot water with the same process, the oil stain removal rate reached 98% in only 15 minutes. However, higher water temperature is not always better — when it exceeds 95°C, some plastics (such as PVC) will slightly soften, which instead makes impurities more likely to stick. This is why the upper limit of the main cleaning temperature is set at 95°C.
Why Does the Removal of Label Adhesives Depend on the Cooperation of Water Temperature and Time?
The label adhesives on plastic bottles are mostly hot-melt adhesives or pressure-sensitive adhesives. Such adhesives gradually lose their viscosity above 60°C, but complete removal requires the cooperation of water temperature and time. Data shows that at 70°C, the peeling time of label adhesives on PET bottles takes 2 minutes; at 85°C, the peeling time of the same type of adhesive can be shortened to 40 seconds.
Why Should the Mesh Aperture of Plastic Washing Lines Decrease Gradually?
 |
In the rinsing tanks, dehydrators and other links of plastic washing lines, screens with different apertures are installed: coarse screens may use 20mm apertures, medium screens 10mm, and fine screens even 3mm. Is this gradually decreasing aperture design just for cleaner filtration? In fact, each layer of the screen undertakes a specific separation task. |
How Can 10mm Coarse Screens Protect Subsequent Equipment?
Plastic fragments from the crusher may be mixed with large particles of impurities such as stones and metal blocks. The 10mm aperture coarse screen can act like a "doorman", first intercepting these hard objects with a diameter exceeding 10mm — if they are allowed to enter subsequent equipment, the rotating parts of the friction cleaner may be damaged, and the drum of the centrifugal dehydrator may vibrate violently due to imbalance.
A washing line once had a damaged coarse screen that was not replaced in time, causing a 15mm diameter steel piece to enter the screw cleaner, directly bending the screw blades, resulting in 20,000 yuan in maintenance costs and 8 hours of downtime. This is why the daily inspection of coarse screens should focus on checking for holes or deformation.
Which Details Affect the Final Result When Using a Plastic Washing Line?
The operation of a plastic washing line may seem to follow a set process, but some easily overlooked details can directly lead to reduced cleaning efficiency, equipment damage, or even safety hazards. These precautions, hidden behind the operation manual, are actually key to ensuring the stable operation of the production line.
Why Can't You Dump All Materials at Once During Feeding?
Many people think that as long as waste plastics are thrown onto the conveyor belt, it's fine. However, the uniformity of feeding directly affects the load of subsequent equipment. When a large amount of plastic rushes into the crusher at once, it may cause the motor to overload and trip; on the other hand, intermittent feeding will leave the friction cleaner short of materials, resulting in "idling" — which not only wastes energy but also causes excessive wear of equipment components due to the lack of material buffer.
Practice at a recycling plant shows that adopting "batch quantitative feeding" (50kg every 30 seconds) can extend the service life of the crusher's blades by 20% and improve cleaning uniformity by 15% compared to "continuous full-load feeding". The correct approach is to use frequency conversion control of the conveyor belt to stabilize the feeding speed within ±5% of the rated value according to the processing capacity of subsequent equipment (e.g., 500kg per hour for the crusher), just like giving the machine a "slow and steady chewing" rhythm.
Why Can't the Concentration of Cleaning Agents Be Added Based on Experience During Chemical Cleaning?
When dealing with stubborn oil stains, some people think "the more cleaning agent, the better the effect", but this approach may backfire. Take sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) as an example: when the concentration exceeds 5%, although the decontamination ability increases, it will corrode the surface of plastics such as PP and PE — under an electron microscope, tiny pits can be seen on the plastic surface, which will instead absorb more impurities.
Experimental data shows that for oil-contaminated PE films, a 3% caustic soda solution achieves a decontamination rate of 95%, while a 5% concentration only increases the decontamination rate to 97%, but the tensile strength of the plastic decreases by 8%. More importantly, excessive chemicals will increase the difficulty of sewage treatment: the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) value will soar from 300mg/L to 800mg/L, doubling the treatment cost. Therefore, chemical cleaning must strictly follow the formula (e.g., 2%-3% caustic soda + 0.5% surfactant), just like administering medicine to a patient — precise dosage ensures both effectiveness and safety.
Why Must the Interior Be Thoroughly Cleaned After Equipment Shutdown?
It is a common misunderstanding to shut down and leave immediately after production is completed. In fact, there is a high probability that a large amount of plastic debris and dirt will remain inside the friction washer, rinse tank and other equipment on the cleaning line. If these residues are not cleaned in time, the residual moisture will cause the metal parts inside the equipment to gradually rust. Boxin paid attention to this key issue and used the more expensive 304 stainless steel for important parts.
The correct shutdown process should be: First, turn off the feeding system to ensure that the equipment can completely empty the internal materials. Then, use clean water to circulate and rinse the equipment for at least 10 minutes. In particular, pay special attention to some dead corners of the friction cleaning machine, and ensure that these places are also thoroughly cleaned. Finally, open the drain valve to completely drain the accumulated water in the equipment. Once a company omitted this critical cleaning step during shutdown, causing the label glue remaining in the rinse tank to solidify gradually. When the machine was turned on next time, the solidified colloid blocked the screen, which eventually caused a 2-hour shutdown time for cleaning, directly resulting in a production loss of up to 1,000 kg. This situation is just like we need to clean tableware after use. The equipment also needs to be thoroughly "cleaned" after "use" to ensure that it can maintain the best working condition when it is used next time.
Why Must Different Plastics Be Strictly Sorted Before Mixed Washing?
When PE film and PET bottle flakes are mixed for recycling, if you use a floating material separation tank, the PET bottle flakes will be regarded as impurities and discharged from the bottom. Therefore, a sorting link must be set up at the front end of the washing line to separate soft and hard plastics through manual or intelligent sorting. This is like "teaching students in accordance with their aptitude", allowing plastics with different characteristics to be cleaned under appropriate processes, taking into account both efficiency and quality.
These operational details may seem trivial, but they run through the entire process of the plastic washing line: the rhythm of feeding controls the "load balance" of the equipment, the concentration of chemical cleaning determines the "boundary between safety and effect", shutdown cleaning is related to the "healthy life" of the equipment, and sorting is the premise of "prescribing the right medicine". Only by understanding and complying with these precautions can the plastic washing line truly play the role of a "purification helper".tant".

 EN
EN 
 English
English 简体中文
简体中文 Русский
Русский España
España عرب .
عرب .